Skip to content
Exposure Keratitis
- May result from any disease process that causes inadequate eyelid closure.
- Causes include:
- Neurogenic diseases such as Bell's palsy, acoustic neuroma.
- Proptosis due to thyroid orbitopathy or other orbital diseases.
- Eyelid dysfunction from restrictive eyelid diseases or previous blepharoplasty.
- Inattentive mental states such as in comatose patients or nocturnal exposure
Clinical Features
- Symptoms:
- Foreign body sensation, itching, burning and conjunctival injection
- Decreased vision
- Pain and photophobia may occur
- Signs:
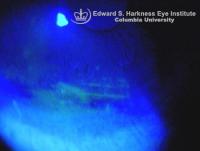
- Superficial punctate epithelial staining involves inferior third of the cornea
- May progress to large area of epithelial defect and complicated with corneal infiltrates, ulceration, perforation or endophthalmitis
Management
- Most important is treatment of underlying cause(s).
- Nonpreserved topical drops during the day and lubricating ointment at bedtime.
- Antibiotic for epithelial corneal defects.
- Lid taping.
- Moisture chamber glasses.
- Temporary tarsorraphy.
- Definitive surgical therapy
Back to top